Advancements in robotics are transforming both healthcare and industry, offering numerous advantages. In healthcare, robots assist surgeons with precision and minimize invasiveness, improving patient outcomes. They can also aid patient care, performing tasks like medication delivery and physical therapy. Robots enhance productivity and safety in industry by automating repetitive and hazardous tasks. They work tirelessly, reducing human error and operational costs. Furthermore, this technology can access tight spaces and handle dangerous materials, making them invaluable in manufacturing and nuclear energy industries—these advancements in robotics promise to improve efficiency, quality, and safety in healthcare and industrial settings.
Noteworthy Robotics Advancements in Healthcare
In the present day, healthcare institutions have a variety of specialized medical robots tailored to perform specific tasks.
Types of Robots
- Surgical assistance robots are engineered to enhance existing surgical techniques, including minimally invasive and orthopedic surgeries. They can be employed in bariatric Surgery, knee and hip replacements, and more.
- Modular robots, exemplified by therapeutic exoskeletons and prosthetic limbs, aid in rehabilitating patients dealing with conditions like stroke, paralysis, traumatic brain injury, and multiple sclerosis. These robots can monitor a patient’s movements during exercises, gauge range of motion, and track progress.
- Service robots assist healthcare professionals by handling routine logistical tasks and providing task completion reports. These tasks encompass preparing patient rooms, managing supplies, processing purchase orders, restocking medical supplies, and transporting linens to and from laundry facilities.
- The increasing trend involves healthcare institutions deploying social robots to engage with patients and visitors in long-term care settings. These robots encourage adherence to treatment plans, offer cognitive stimulation, boost patient morale, and guide visitors and patients within healthcare facilities.
- Mobile robots perform various duties throughout hospitals or clinics, following predefined tracks or wires, while physicians remotely control autonomous robots.
Pioneering Robotic Inventions
Numerous robotic systems, such as the da Vinci Surgical System and TUG, have become popular in healthcare settings worldwide. The da Vinci Surgical System is notable for its advanced 3D vision and exact instruments that perform tasks more intricate than human hands.
Meanwhile, TUG is a clever autonomous robot that can independently transport heavy items like medications and lab samples, controlled via a user-friendly touch screen. It completes over 50,000 deliveries weekly across 140+ U.S. hospitals. Other impressive robots like SAM (a helpful guide), Pharm ASSIST ROBOTx (for medication management), Xenex (for disinfection), and Origami (a capsule robot) offer diverse solutions.
Automated Functions Performed by Robots
Robots are designed to carry out numerous essential tasks in healthcare. They can engage with patients, assess their living conditions, work in hazardous emergencies, analyze data to improve pharmacy operations, and sanitize hospital rooms. These programmed functions help enhance patient care and overall healthcare efficiency.
Robots interact with patients, providing support and companionship while assessing their living environments’ quality for better care planning. In emergencies, robots step in, ensuring safety and efficiency under challenging conditions. Moreover, they are vital in optimizing pharmacy operations by mining data for more intelligent resource allocation.
High-quality health care
Medical robots are a boon in healthcare, aiding in minimally invasive surgeries, personalized monitoring for chronic patients, innovative therapies, and engagement. Nurse robots, resembling human nurses, excel in performing tasks tirelessly, freeing up human nurses and caregivers from routine duties. It allows healthcare professionals to concentrate on essential responsibilities, including meaningful human interactions and emotional support, contributing to patients’ overall long-term health and happiness.
Work Environment Safety
Nurse robots, responsible for bed-moving and patient lifting, reduce workplace dangers for healthcare employees. Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) are used for ferrying supplies and linens within hospitals, especially in areas where contact with harmful pathogens is a worry. This approach serves to protect healthcare workers from potential harm. Additionally, cleaning and disinfection robots are vital in reducing hospital-acquired infections and limiting the chance of exposure to harmful microbes. In turn, it creates a safer healthcare setting for patients and the dedicated professionals tending to their needs.
Simplified Clinical Workflows
Autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) alleviate the physical strain on human workers and bring greater consistency to various processes. They offer a solution to staffing shortages by efficiently managing inventory and promptly requisitioning supplies, equipment, and medications at suitable locations. In addition, disinfection and cleaning AMRs swiftly sanitize hospital rooms, making them ready for new patients. This capability allows human workers to concentrate on patient-centered and value-driven tasks, enhancing overall healthcare service quality.
Robotic Surgery using Surgical Robots
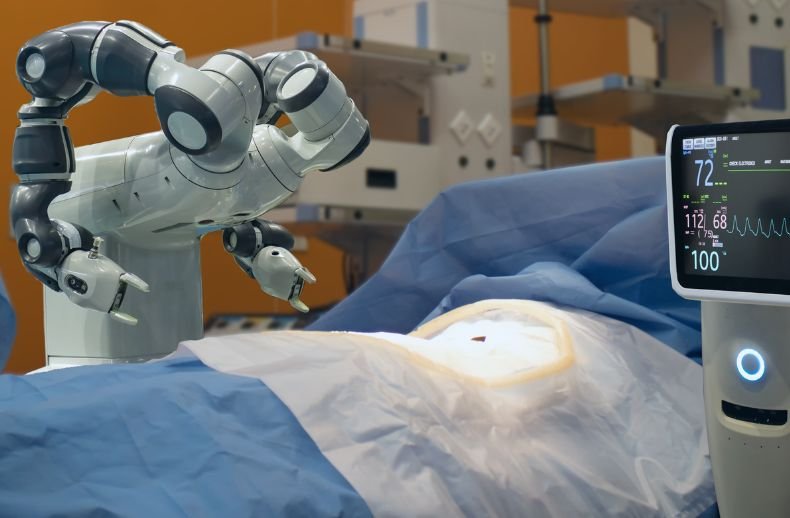
Robots have evolved to assist in preparing the surgical setup and actively participate in medical procedures, enhancing precision for general surgeons. These surgical robots offer surgeons greater flexibility, precision, visual clarity, and control during complex surgeries. Robotic Surgery, in particular, has reduced infection risks and shortened hospital stays due to smaller incisions. Additionally, robot-assisted procedures lead to less blood loss, fewer transfusions, and faster patient recovery. Patients can leave the hospital sooner and recover quicker. Robots are finding increasing applications in healthcare.
Robotic assistance for a better life
In healthcare, robotics goes beyond tasks like blood draws and transporting items. Remote-controlled medical robots enable caregivers to engage with patients, assess their living conditions, and determine if follow-up appointments are needed. It boosts efficiency by eliminating the need for time-consuming home visits. Examples include Canada’s use of companion robots like Ludwig since 2016 and elderly care facilities in Ireland introducing Stevie to residents. Numerous social robots are employed in elderly care, showing the expanding role of robotics advancements in healthcare.
Conclusion
Robotics has ushered in a transformative era in healthcare, offering many benefits. Specialized medical robots perform critical tasks, from surgeries to patient rehabilitation and logistical support. Innovative inventions like the da Vinci Surgical System and TUG have become invaluable assets in healthcare institutions worldwide.
These robots enhance patient care, improve work environments, and streamline clinical workflows. Robotic Surgery minimizes risks, shortens recovery times, and enhances surgical precision. The continued evolution of robotics in healthcare holds great promise for improving overall healthcare quality and patient outcomes.